The conveyor belt is a fundamental component of modern industrial operations, streamlining processes across various sectors. From manufacturing to logistics, conveyor systems ensure efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance productivity. This article explores the history, types, and applications of conveyor belts, delving into their significance in today’s fast-paced industries.
What Is a Conveyor Belt?
A conveyor belt is a continuous moving system used to transport materials from one location to another. It consists of a belt looped around rollers or pulleys, powered by an electric motor.
Key Features of Conveyor Belts:
- Efficiency: Moves materials quickly and consistently.
- Versatility: Adapts to different industries and materials.
- Durability: Built to withstand heavy loads and harsh conditions.
From transport belts to industrial conveyor systems, these belts play a vital role in material handling.
The History of Conveyor Belts
The concept of conveyor belts dates back to the late 18th century, evolving into the advanced automated belt systems we see today.
Key Milestones:
- 1795: The first primitive conveyor belts were used to transport grain in ports.
- 1901: Sandvik introduced the first steel conveyor belt.
- 20th Century: Conveyor belts became integral to assembly lines, revolutionizing industries like automotive manufacturing.
- Modern Era: Advanced materials and automation have made conveyors more efficient and versatile.
The evolution of the assembly line belt highlights its importance in industrial progress.
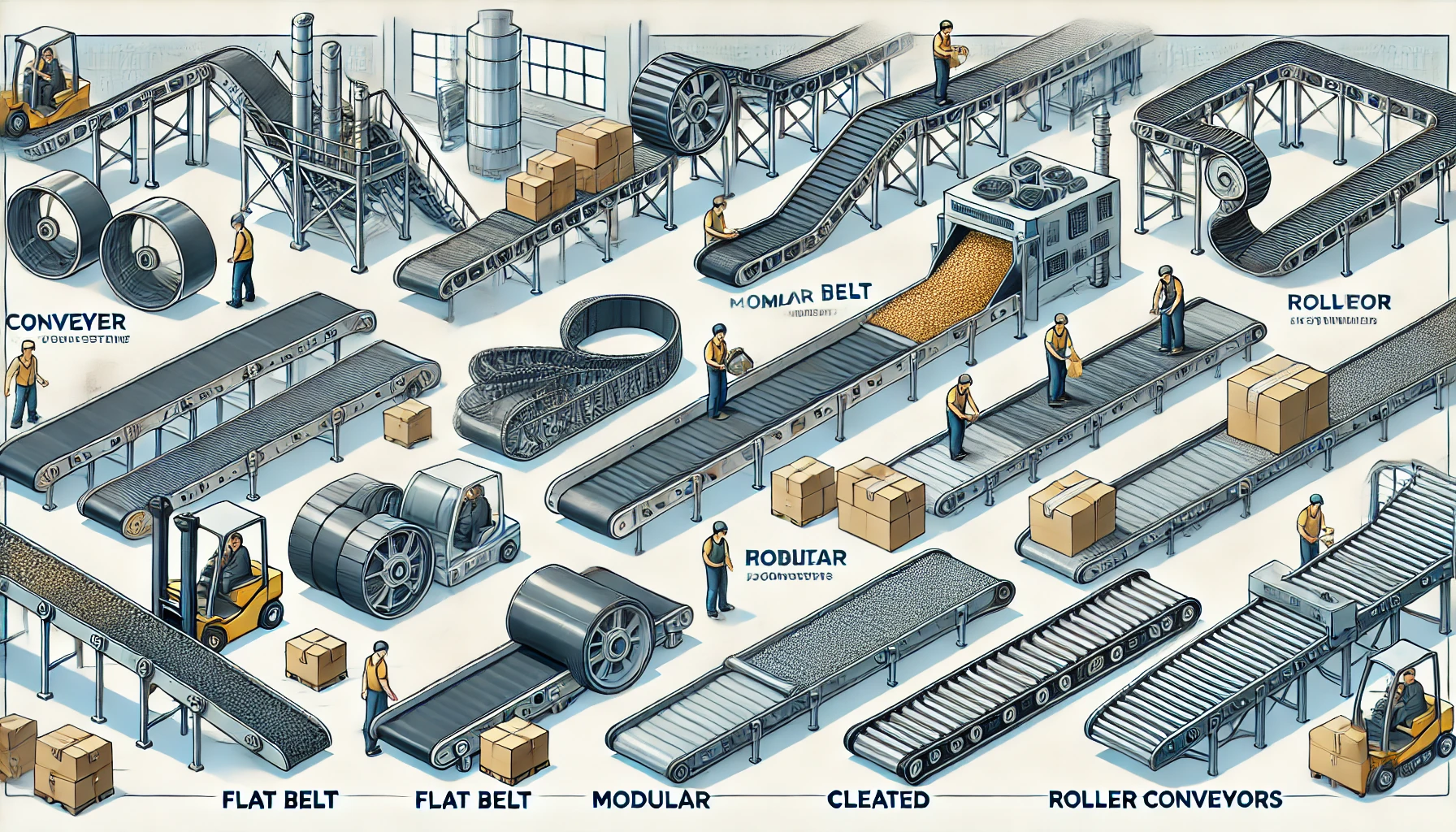
Types of Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
1. Flat Belt Conveyor
- Use: Common in manufacturing and warehousing.
- Features: Ideal for transporting lightweight goods.
2. Modular Conveyor Belt
- Use: Suitable for food processing and packaging.
- Features: Made of interlocking segments for easy cleaning.
3. Cleated Conveyor Belt
- Use: Transports materials at steep angles.
- Features: Equipped with raised sections to prevent sliding.
4. Roller Bed Conveyor
- Use: Used in logistics and shipping.
- Features: Reduces friction for heavy loads.
5. Inclined Belt Conveyor
- Use: Moves materials between different height levels.
- Features: Designed with grooves or cleats for better grip.
These variations demonstrate the adaptability of belt conveyors across industries.
Applications of Conveyor Belts
The conveyor system is used in diverse sectors to improve operations and efficiency.
1. Manufacturing
- Automates production lines for consistent output.
- Examples: Automotive assembly, electronics manufacturing.
2. Warehousing and Logistics
- Streamlines inventory management and shipping processes.
- Examples: Sorting facilities, distribution centers.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
- Ensures hygienic transport of products.
- Examples: Processing lines, packaging plants.
4. Mining and Construction
- Handles heavy materials like ores and gravel.
- Examples: Quarry operations, cement plants.
5. Pharmaceuticals
- Ensures precision in transporting delicate products.
- Examples: Pill sorting, packaging systems.
The versatility of industrial belt systems makes them indispensable across these industries.
Advantages of Conveyor Belts
The widespread adoption of moving belts stems from their numerous benefits:
1. Increased Efficiency
Conveyor belts reduce the time and effort needed to move materials, boosting productivity.
2. Cost-Effective
By automating processes, conveyor systems lower labor costs and minimize errors.
3. Improved Safety
They reduce the risk of workplace injuries by eliminating the need for manual handling.
4. Customizable
Production line conveyors can be tailored to specific operational needs.
These advantages make conveyor belts a cornerstone of modern industrial operations.
How to Maintain Conveyor Belts
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of material handling belts.
Tips for Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Check for wear and tear on belts and rollers.
- Lubrication: Keep moving parts well-lubricated to reduce friction.
- Alignment: Ensure the belt runs smoothly without deviation.
- Cleaning: Remove debris and residue to prevent clogging.
Following these practices minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of your industrial conveyor.
Innovations in Conveyor Systems
Modern automated belt systems incorporate advanced technologies to enhance performance:
1. IoT Integration
- Real-time monitoring of conveyor operations.
- Enables predictive maintenance to prevent breakdowns.
2. Energy Efficiency
- Eco-friendly designs reduce power consumption.
- Examples: Solar-powered conveyor systems.
3. Smart Materials
- Use of lightweight yet durable materials for better performance.
These innovations make transport belts more reliable and sustainable.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Conveyor Belts
The conveyor belt has transformed industries by automating material handling and improving efficiency. From flat belt conveyors in manufacturing to cleated conveyors in construction, these systems cater to a wide range of needs. With advancements in technology, conveyor belts continue to evolve, driving industrial progress. Investing in a reliable conveyor system ensures streamlined operations and long-term success.
FAQs About Conveyor Belts
1. What is a conveyor belt?
A conveyor belt is a moving system used to transport materials efficiently.
2. What are the main types of conveyor belts?
Common types include flat belts, modular belts, cleated belts, and roller conveyors.
3. Where are conveyor belts used?
They are used in manufacturing, logistics, food processing, mining, and more.
4. How do you maintain a conveyor belt?
Regular inspections, lubrication, alignment, and cleaning help maintain conveyor belts.
5. What are the advantages of conveyor belts?
They improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, enhance safety, and are customizable for various applications.